Tensioners and Sliders
Tensioners and Sliders
Prepared by
Dr.Aparna Kulkarni(PT)
Dr.Meena Nair(PT)
Dr.Aparna Kulkarni(PT)
Dr.Meena Nair(PT)
Neural Mobilization
- Mobilization of nervous system is an approach to physical treatment of pain.
- This technique propose to reduce Mechano-sensitivity by improving the ability of neural tissue to tolerate mechanical force during movement (NEE et al 2011)
- Neural mobilization techniques are used to decrease adverse mechanical tension on the nerve
- This technique frees up the nerves which so that it can slide in it’s sheath.
Physiological effects of Neural Mobilization
- Restore the dynamic balance between the relative movement of neural tissues and surrounding mechanical interfaces
- Facilitation of nerve gliding
- Reduction of nerve adherence (viscoelastic properties)
- Dispersion of noxious fluids
- Increased neural vascularity (intraneural bloodflow)
- Improvement of axoplasmic flow
Two types of techniques are commonly used treating patient with nerve related pain
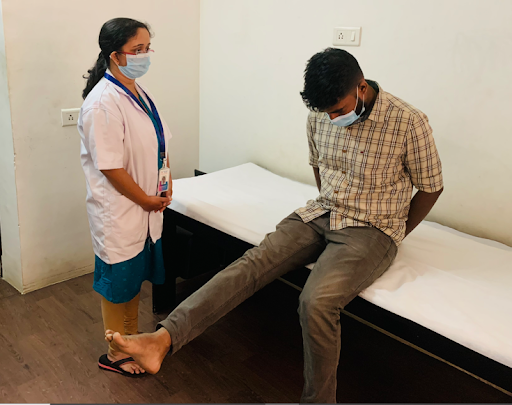
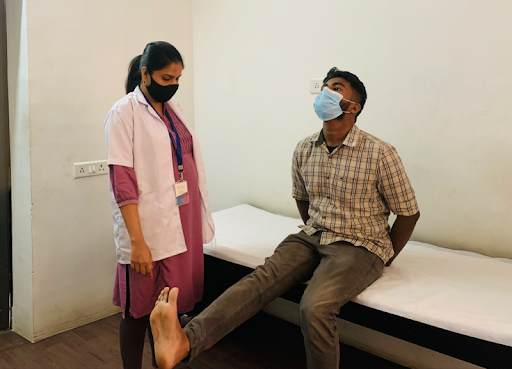
Tensioners
It’s a neurodynamic test that produces tension in the neural structure
Sliders
Neurodynamic manoeuvre to produce sliding movement of neural structure relative to their adjacent tissues.
Effects of Tensioner
- Involve elongation of nerve bed.
- Beneficial effects by pumping action of nerve.
- Reduce intraneural pressure and improve circulation. (Coppieters et al 2008)
- Produces tension in neural structure but does not surpass the elastic limit.
- Activate viscoelastic, movement related and physiological function in nervous system.
Effects of Sliders
- Involve combination movement at different joint.
- Elongation of one nerve bed is balanced by reduction in length of nerve bed at another joint.
- Less aggressive technique.
- Appropriate for acute conditions and post-operative management.
- Reduction in nerve tension limit the possibility of causing nerve irritation and inflammation. (Coppieters et al 2008)

Indication
- Used in non irritable condition ( Neuropathic/ Neurogenic)
- For patho-mechanical causes.
- Fibrosis
- Connective tissue adhesion.
- Restriction of normal tissue mobility.
Contraindication
- Malignancies of the nervous system or vertebral column
- Acute inflammatory infections.
- Areas of instability.
- Spinal cord injuries.
- Suspected disc lesions.
- Cauda equina lesions.
- Dizziness related to VBI.
- Any central nervous system disorder( Spina bifida, MS)
